Daniel Brockley
Daniel Brockley
What is a trust, and what are the different types of trusts?
Trusts come up a lot in estate planning, and for good reason. They can be incredibly effective in helping fund education, provide for heirs, donate to charities and more. For high net worth individuals, trusts are also an important strategy to reduce taxable estates.
What are trusts?
Trusts are legal entities, much like corporations, which are considered distinct from the various parties involved. Trusts come in many forms, but in essence they are fiduciary arrangements in which, as the IRS states, “one person (the trustee) holds title to property or assets…for the benefit of another (the beneficiary).” The person who creates the trust is called the settlor, sometimes also referred to as the grantor or trustor. Sometimes the settlor is also the trustee, while in other cases the trustee is a third party. Trusts can be used to dictate the flow of a person’s assets during life, after death, or both.
Quick-reference definitions:
Settlor (or grantor): the person who creates the trust.
Trustee: the person who manages the property or assets in the trust.
Beneficiary: the person or people who will receive the assets in the trust.
There are many reasons people choose to employ trusts as a part of their financial and estate planning strategies. For one, trusts are typically not subject to probate, the court supervised process triggered upon a person’s death which involves the appointment of an executor or personal representative and the administration and validation of their will (if one exists). This process can be time consuming as well as expensive – and the probate process is a public process, meaning anyone can find out to whom and how much you’ve left behind. So, those wishing to keep the assets of their estates private, often place them in a trust.
Another reason for using trusts is control, both during life and after death. When a trust is created, the person setting up the trust dictates the terms of that trust, including who will receive distributions from the trust, when those distributions will occur, and on what terms. Additionally, depending on the type of trust, trusts can also be a valuable tool for tax planning.
Revocable vs irrevocable trusts
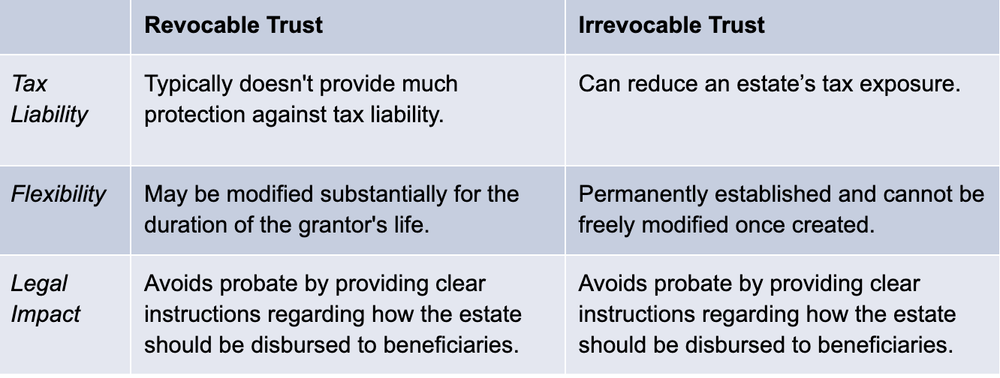
The two primary types of trusts are revocable – those that can be altered by the grantor during their lifetime – and irrevocable – those in which the grantor relinquishes all control over the trust once it’s been enacted. These two primary types of trusts have different pros and cons.
Pros and cons of revocable trusts
Revocable trusts can be changed anytime during a grantor’s lifetime, and the grantor continues to have access to the assets in the trust, making them more flexible than irrevocable trusts. A revocable trust is typically used for planning purposes as well as peace of mind (knowing that should the grantor become incapacitated or incompetent, there will be a successor trustee to step in and help manage their affairs). They are also used to avoid probate when the grantor dies. However, while they offer a greater level of flexibility, they do not remove assets from the grantor’s taxable estate, and thus are not as effective in reducing tax liability.
Pros and cons of irrevocable trusts
As the name implies, irrevocable trusts cannot be altered once established. They are generally used to take money out of a grantor’s estate and permanently give it to a beneficiary, thus lowering the tax liability of the grantor while providing for the beneficiary.
Here are a few of the commonly used trusts in estate planning:
1. Grantor retained annuity trusts: GRATs
A grantor retained annuity trust allows the grantor to put appreciable assets in a trust and receive an annual annuity payment for a specified term of years. At the end of the specified term of the GRAT, if the grantor survives the trust term, the remaining assets will be transferred to the named remainder beneficiary free of transfer tax.

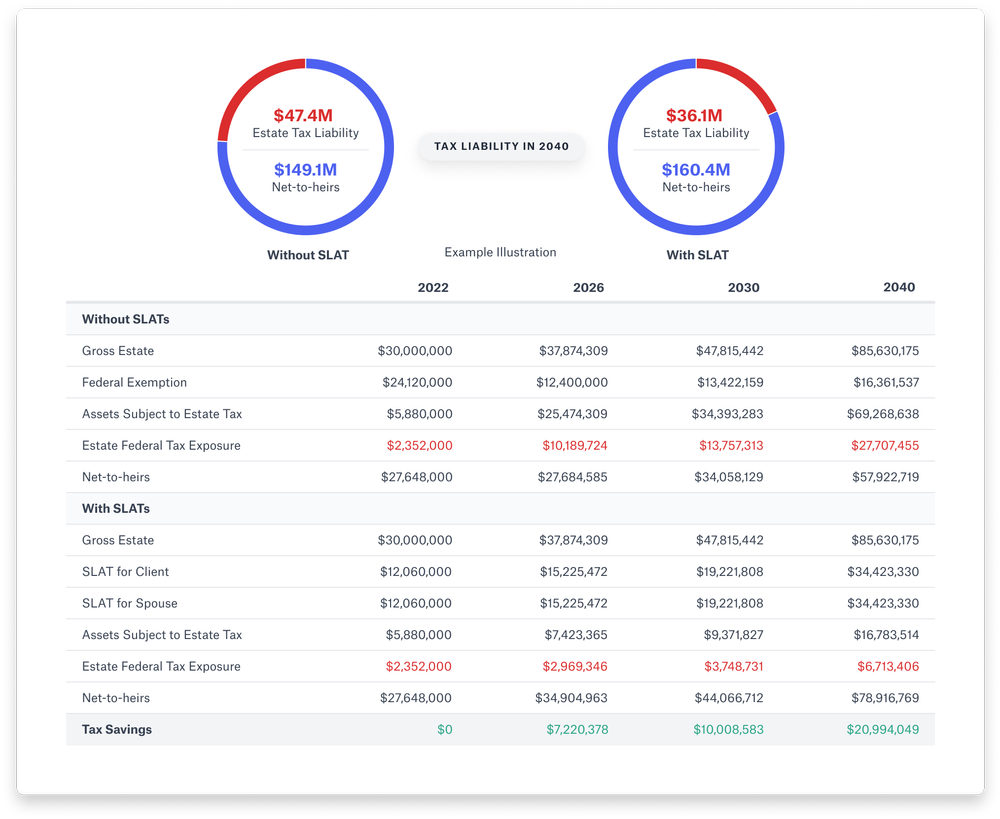
2. Spousal lifetime access trusts: SLATs
The spousal lifetime access trust is an irrevocable trust in which one spouse (the settlor) puts assets into the trust that the other spouse (the beneficiary) can then access. This takes the assets in question out of the settlor’s taxable estate but still allows the spouse to access the funds at will. It’s implied that the settlor may also be able to access those funds through their spouse, thereby giving the couple the flexibility to make use of the money when needed while keeping it out of the taxable estate or the reach of creditors.
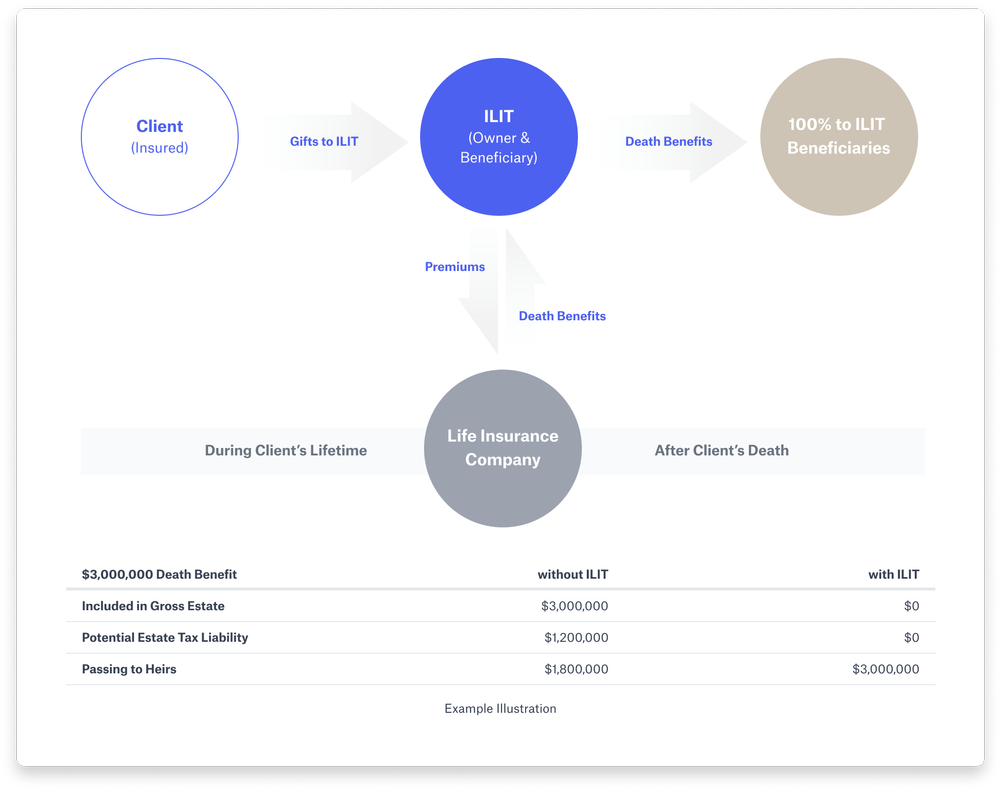
3. Irrevocable life insurance trusts: ILITs
In an irrevocable life insurance trust, the settlor transfers or buys a life insurance policy in a trust, so it is then fully “owned” by that trust and no longer considered a part of his or her estate for estate tax purposes. When the trust is created, it will outline how benefits will be distributed upon the insured’s death – or sometimes upon a second death (a spouse). Once an ILIT is created, being an irrevocable trust, it cannot be altered.
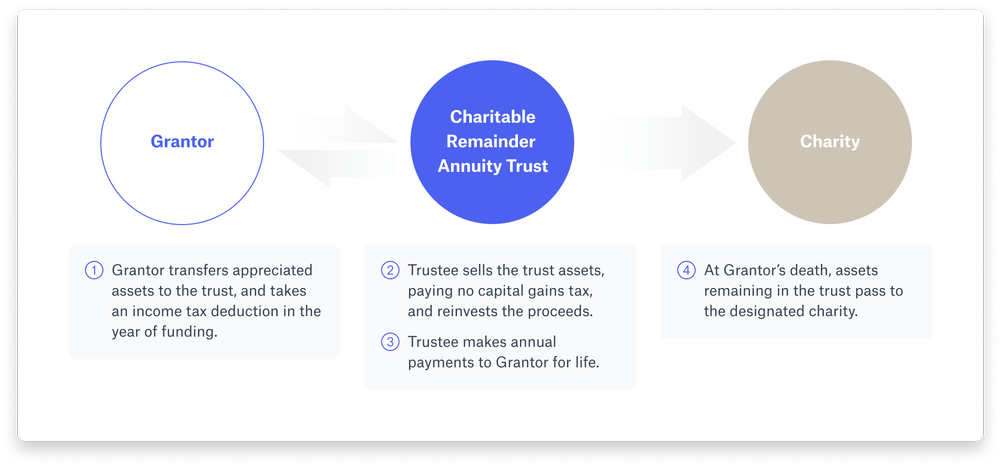
4. Charitable remainder trusts: CRTs
In a charitable remainder trust, a settlor makes an irrevocable gift to the trust. During the trust term, the settlor receives an annual payment back from the trust, and at the trust’s termination all remaining assets are distributed to charities designated in the trust. The settlor receives a current income tax deduction for the gift to the trust. The amount of the income tax deduction is the present value of the future interest that the charity will ultimately receive at the end of the trust term as determined using a predetermined rate set by the IRS.
5. A/B trust arrangement
A common trust arrangement used by married couples to minimize estate taxes for the surviving spouse after one spouse passes away the A/B trust arrangement, also known as a “spousal and bypass trust” or “marital and bypass trust,” incorporates the use the two trusts: the marital, or “A” trust and the bypass trust, or “B” trust.
Upon the death of the first spouse, the estate is divided into two portions. The Marital trust “aka A trust” portion holds the assets intended to benefit the surviving spouse while they are alive, while ensuring that after the death of the surviving spouse the remaining assets are ultimately distributed according to the settlor’s wishes. The surviving spouse can receive income from the trust and, in some cases, have access to principal for their needs. The A trust is typically not subject to estate taxes upon the death of the first spouse due to the unlimited marital deduction, effectively delaying any payment of estate tax until the death of the surviving spouse.
The Bypass trust / credit shelter trust (aka B trust) holds the assets usually up to the federal estate tax exemption amount, effectively using the deceased spouse’s federal exemption. The assets in the bypass trust and any subsequent growth on those assets are shielded from estate taxes upon the surviving spouse’s death, as they are not considered part of their estate, essentially “bypassing” the surviving spouse’s estate. The surviving spouse can still benefit from the trust’s income and, upon their death, the remaining assets pass to the designated beneficiaries, often the couple’s children.
This A/B trust arrangement allows married couples to maximize the use of their federal estate tax exemptions and potentially reduce the overall tax burden on their estates. It also ensures that the intended beneficiaries, often the couple’s children or other designated individuals, receive the remaining assets after both spouses have passed away.
6. Disclaimer Trust
A Disclaimer Trust allows a spouse to refuse (or disclaim) part or all of an inheritance. This refusal helps to minimize estate taxes and control asset distribution. The disclaimed assets pass into an irrevocable trust, and keep the assets out of the spouse’s taxable estate. Disclaimer trusts offer flexibility to adjust the estate plan post-death, depending on the circumstances at the time, including the spouse’s financial situation or changes in tax law. It’s critical to execute the disclaimer properly, within a certain time frame, to avoid adverse tax implications.
7. Domestic asset protection trust (DAPT)
A Domestic Asset Protection Trust (DAPT) is a type of trust established in certain states that provides asset protection benefits for the settlor. With a DAPT, the settlor transfers assets into the trust while retaining certain beneficial interests. The key feature of a DAPT is that it offers protection against creditors, meaning that the assets held within the trust are shielded from potential future claims or legal actions. Unlike traditional trusts, a DAPT allows the settlor to be a discretionary beneficiary, enabling them to access the trust’s assets if needed. However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of a DAPT may vary based on the specific laws and regulations of the state in which it is established.
8. Pot trust
A pot trust is a single trust for all beneficiaries (typically children and more remote descendants). Distributions can be made to any beneficiary at the trustee’s discretion. This trust structure allows for greater flexibility in managing the needs of all descendants collectively. For example, one branch of the family may have greater needs than another branch of the family. By using a pot trust, it allows the trustee to provide more resources to the branch that has greater needs. This trust continues until required to terminate by state law.
9. Qualified Terminable Interest Property (QTIP) Trust
Often a marital trust is structured as a qualified terminable interest property (QTIP) trust. In a QTIP trust, the surviving spouse receives income from the trust during their lifetime, and upon their death, the remaining assets are distributed to the beneficiaries designated by the settlor. This type of trust allows the settlor to provide financial security for their spouse while maintaining control over the final distribution of assets, making it a useful tool for estate planning and minimizing estate taxes.
10. Special needs trust
A special needs trust, also known as a supplemental needs trust, is a legal arrangement established to provide for individuals with disabilities or special needs. The trust is designed to hold assets and provide for the financial well-being of the beneficiary without jeopardizing their eligibility for government benefits like Medicaid or Supplemental Security Income (SSI). The trust is managed by a trustee who disburses funds to supplement the beneficiary’s needs not covered by public assistance programs. This may include medical expenses, education, therapy, personal care attendants, transportation, and recreational activities. By ensuring continued access to vital government benefits while providing additional support, special needs trusts can enhance the quality of life and care for individuals with disabilities.
11. Qualified personal residence trust
A Qualified Personal Residence Trust (QPRT) is a legal tool that allows a homeowner to transfer their primary residence or vacation home into a trust while still living in it for a predetermined period. This enables the homeowner to remove the property’s value from their taxable estate, potentially reducing estate taxes. At the end of the trust term, the property passes to the trust beneficiaries, typically family members, at a lower value for gift tax purposes. If the homeowner dies during the trust term, the property is brought back into their estate. It is important to note, that at the end of the trust term, the settlor/homeowner will need to rent or lease the property from the beneficiaries in order to continue using the property.
12. Generation skipping trust (GST)
The generation-skipping transfer tax (or “GSTT”) imposes an additional 40% tax on assets gifted to a grandchild or great-grandchild, or anyone unrelated who is 37.5 years or more younger than the donor. The GSTT is imposed on gifts made directly to those individuals, but is also on gifts to certain trusts that can benefit those individuals. The GSTT was established to combat people getting around the estate tax by putting a large pool of assets into a multi-generational trust, which would then never be taxed again. A generation skipping trust can be used to help minimize the estate and GST taxes when passing assets and money on to a later generation.
Simplifying the complexities of estate planning
There are many kinds of trusts, and it’s not uncommon for people to use several different trusts as a part of their estate plans. It can get complicated to understand the implications and the flow of funds. That’s why it’s important to work with a top-notch financial advisor and estate attorney, bolstered by the right technology. Vanilla can help by enabling you to visualize the full scope of your balance sheet and estate, using easy to understand graphs and charts to show the flow of funds and highlight opportunities. Financial advisors interested in Vanilla can schedule a demo to learn more.
About Vanilla
Vanilla is the Estate Advisory Platform, purpose-built to enable financial advisors to build deeper relationships with their clients and empower clients to build and protect their legacy. From robust and easy-to-understand visualizations of complex estates, detailed diagrams of how assets transfer to future generations, to ongoing estate monitoring, Vanilla is reinventing the estate planning experience, end-to-end. Learn more about Vanilla at https://www.justvanilla.com/.
Media inquiries: Please contact press@justvanilla.com
This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered legal advice. If you feel that the information in this article is pertinent to your situation, you may wish to consult a qualified attorney for advice tailored to your circumstances.
FAQs
What is right for me: Joint revocable trust vs individual revocable trust?
A joint revocable trust is the most common option for married couples with children from the same marriage, who live in community property states, and who do not have significant separate property. A joint revocable trust treats you and your spouse as a single unit and is easy to manage for couples who own assets jointly. A joint revocable trust allows you and your spouse to specify how your assets should be handled during your lifetimes, as well as how they are distributed upon each of your deaths. Assets can be added or removed from the trust throughout your lifetimes and the trust can be amended as needed. Even if you are married in a community property state, a joint revocable trust may not be the right selection if
- this is a second marriage and you have children from the prior marriage
- you have significant separate property
- expect to receive significant separate property (i.e. a large inheritance)
- you have a premarital agreement
An individual revocable trust is the most common option for individuals (including married couples) who reside in a separate property state. An individual revocable trust allows you to specify how your individual assets should be managed during your lifetime, as well as how they are distributed upon your death. Assets can be added or removed from the trust throughout your lifetime and the trust can be amended as needed.
Should I leave my assets in trust or outright to my spouse or kids?
When considering whether to give your spouse assets outright or in trust at your death, you should consider a number of factors, such as:
– Creditor Protection: By placing the assets in a trust, it provides a layer of protection for your assets that is not available if your spouse receives those assets outright. For example, if your spouse is a professional (e.g. doctor, lawyer, etc.), and is sued in their personal capacity, their individually owned assets may be subject to the claims of the creditor. Another example would be if your spouse was in a car accident and was sued by the injured party; their individually owned assets may be subject to the claims of the creditor. Additionally, if your spouse remarries, any assets in trust will be protected from division in a divorce.
– Control Over Remainder: By placing the assets in trust, you can control who receives the remainder of the trust at your spouse’s death. For example, if you have children from a prior relationship, and you want them to receive the assets after your spouse passes away, a trust allows you to direct that the remaining assets in the trust go to your children at your spouse’s death. If your spouse receives the assets outright, your spouse will be free to spend or give away the assets to whomever they please during life and at their death.
– Tax Planning: A trust allows you to maximize the benefit of your tax exemptions (e.g. the gift and estate tax exemption), which you may otherwise be unable to fully use if you gave your spouse the assets outright.
It is important to note that if you leave your spouse assets in trust, the trust has to be drafted to ensure that it qualifies for the unlimited marital deduction between spouses. If the trust does not contain specific provisions, it may inadvertently result in the trust not qualifying for the unlimited marital deduction, therefore leaving the assets subject to estate tax at the first spouse’s death.
Published: Nov 17, 2022
Holistic wealth management starts here
Join thousands of advisors who use Vanilla to transform their service offering and accelerate revenue growth.