Vanilla
Vanilla
What is a grantor retained annuity trust (GRAT)?
In a grantor retained annuity trust (GRAT) , a grantor transfers a particular asset(s) into an irrevocable trust and retains an annuity stream from the trust for a specified term of years. The annuity amount is calculated based on an IRS interest rate (referred to as the “hurdle rate”). At the end of the trust’s term, if the grantor survives the term of the trust, any assets remaining in the GRAT (the appreciation above the hurdle rate) will pass transfer-tax-free to the named “remainder beneficiary”, generally a trust for family members.
How does a GRAT work?
Grantor retained annuity trusts (GRATs) have increased in popularity in recent years because of how effective they are in transferring assets out of estates to beneficiaries in a tax-efficient manner. GRATs allow an individual grantor to transfer an asset’s upside out of their estate, with minimal risk or downside. Using this strategy, the GRAT transfers the initial value of the asset plus a government rate out of the grantor’s estate.
The “Walton” GRAT
Unlike trusts intended to exist until or after a grantor’s death, a GRAT has a specified term of at least two years, but can be for any duration.
When the trust is funded, the grantor is considered to have made a taxable gift to the remainder beneficiary equal to the value of the assets transferred, less the value of the grantor’s retained annuity payments. The value of the retained annuity payments are calculated using the IRS’s 7520 Interest Rate, also referred to as the hurdle rate.
However, the value of the retained annuity payments is often structured to nearly equal the value of the property transferred to the GRAT, so in essence the GRAT will pay back the grantor 100% of the transferred property plus the 7520 rate. In these cases, there should be no taxable gift on funding because the value of the remainder interest has been “zeroed-out”. A GRAT that is zeroed-out is sometimes called a “Walton GRAT,” named after the court case that confirmed that GRATs could be structured in this manner.
When grantor retained annuity trusts(GRATs)are the right choice
A GRAT may be an ideal estate planning technique if an individual is interested in transferring the appreciation of an asset out of his or her estate, while reducing estate tax liability on the individual’s death. GRATs are typically appropriate if the grantor has already used all of his or her gift tax exemption, or if the grantor has a concentrated or volatile asset.
How does a GRAT work?
Here’s a fictional example of how a GRAT might work:
Jane is an executive at the public company “ABC”, and has accumulated significant ABC stock after years of working there. The company is a high-growth business that has increased in value significantly but whose price is also very volatile. Jane would like to do some estate planning but does not want to use her federal gift tax exemption to transfer the stock into a trust knowing there is a risk that it may go down in value after the transfer; thereby wasting a portion of her exemption.
Jane chooses to fund a GRAT, because she knows that only the appreciation over the term of the trust will transfer out of her estate, and, by using a Walton GRAT she will not use any of her remaining estate tax exemption. Jane also knows that if ABC is worth less than the value of the stock when the GRAT was initiated, then all of the stock will be returned to her and she will have the option to re-GRAT her holdings in ABC again in the future.
Jane chooses a two-year GRAT and puts $1,000,000 of ABC in the GRAT. On the first anniversary of the GRAT, Jane receives an annuity distribution of approximately $500,000 in ABC stock plus the equivalent value of the 7520 rate. The annuity can be paid to her in-kind with ABC stock. Because the GRAT is a grantor trust to Jane, there are no income tax consequences on the transfer to the GRAT or the annuity payment(s) to Jane.
Tax benefits of a GRAT
If, at the end of the term of the GRAT, the stock is worth approximately $2M, then $1M transfers to a trust for the beneficiaries determined by Jane and Jane used zero Federal gift and estate tax exemption to make this transfer
However, if the stock has decreased in value during the term of the GRAT, then Jane will have received all of the shares of ABC back in the form of annuity payments
It is important to note that the basis of any assets transferred to a remainder beneficiary via a GRAT will not receive a step-up in basis at the grantor’s death.
Advanced GRAT strategies for estate planning
Most GRATs grant the grantor the power to substitute assets of equal value in the trust. This provision can be a potent tool for proactive advisors.
To illustrate the point, let’s assume a very volatile stock is valued at $10 per share on the date of its contribution to a GRAT, and the Grantor does not want to sell the stock. Next, let’s suppose that during the two-year term, the stock appreciates to $20 per share, then falls to $2 per share, then rises again to $20 per share before the end of the GRAT term where it settles back in at $10 per share.
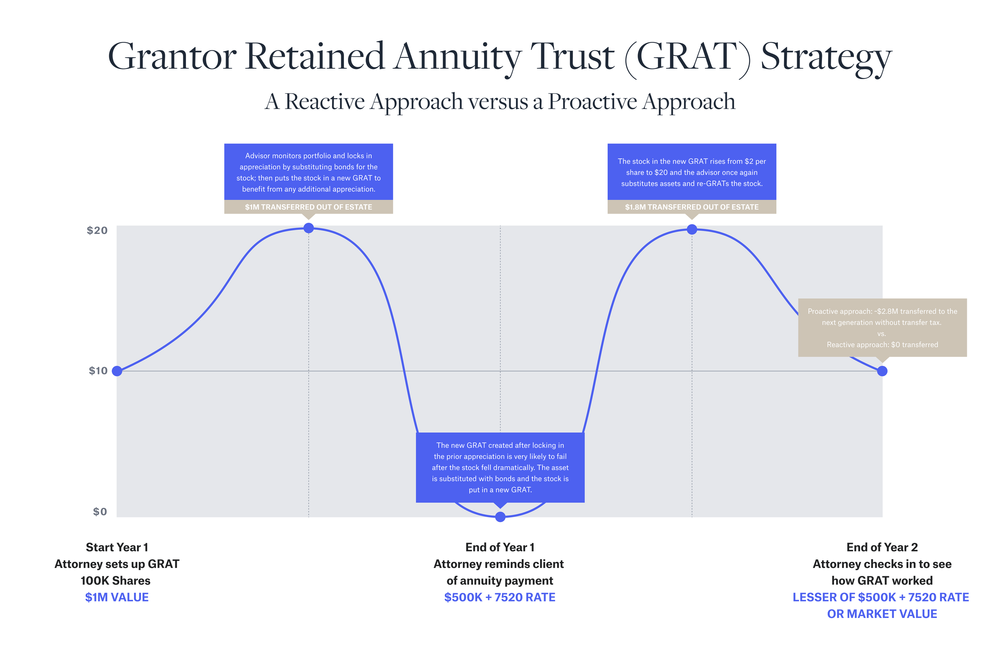
With a wait-and-see approach, the GRAT will mature without transferring any assets out of the grantor’s estate because the value at the end of the GRAT term is equal to value at the time of the original contribution. But a vigilant, savvy advisor could use a few simple steps to capitalize on the volatility of the stock when he or see sees a sharp increase in price.
For example, a GRAT freeze can be accomplished by substituting a low-volatility asset for the stock, and re-GRATing the stock into a new GRAT. By doing this, one can lock in gains before the end of the GRAT term and continue to enjoy further appreciation. The same technique could be used to “reset” a GRAT that is likely to fail if the value of the GRAT assets fall too far below the initial contribution.
Using our hypothetical illustration, the savvy advisor moves almost $2.8 million to the next generation without tax, while the less proactive approach yields $0. This technique can be repeated over and over, capitalizing on the asset price movement.
Grantor retained annuity trust calculator
Determine the amount of the annuity payments:
- The grantor selects a fixed annuity payment amount that they will receive annually from the GRAT during its term.
- The annuity payments can be a fixed dollar amount or a percentage of the initial value of the assets transferred to the GRAT.
- The annuity payments must be made at least once a year and remain constant throughout the term.
Calculate the present value of the annuity payments:
- The present value of the annuity payments represents the current value of the stream of future payments.
- The present value is calculated using the chosen annuity payment amount and the applicable federal rate (AFR).
- You can use an online calculator to help you determine the present value based on these variables.
Determine the remainder interest:
- The remainder interest is the value of the assets that will pass to the beneficiaries after the annuity payments have been made.
- To calculate the remainder interest, subtract the present value of the annuity payments from the initial value of the assets transferred to the GRAT.
Evaluate the gift tax implications:
- The grantor is deemed to have made a gift to the beneficiaries equal to the remainder interest.
- If the present value of the remainder interest is lower than the initial value of the assets, the gift tax liability will be reduced or eliminated.
Be sure to consult with a qualified advisor or estate planning professional to understand the specific gift tax implications based on your circumstances and jurisdiction.
Simplifying the complex
GRATs are powerful financial instruments and may be ideal for a client’s circumstances. Each situation is unique, and investors should consider all aspects of their estate when making a decision. Vanilla provides you with tools to make complicated financial advice understandable in many diverse situations.
About Vanilla
Vanilla is the Estate Advisory Platform, purpose-built to enable financial advisors to build deeper relationships with their clients and empower clients to build and protect their legacy. From robust and easy-to-understand visualizations of complex estates, detailed diagrams of how assets transfer to future generations, to ongoing estate monitoring, Vanilla is reinventing the estate planning experience, end-to-end. Learn more about Vanilla’s estate planning software.
Media inquiries: Please contact press@justvanilla.com
This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered legal advice. If you feel that the information in this article is pertinent to your situation, you may wish to consult a qualified attorney for advice tailored to your circumstances.
Published: Jan 17, 2023
Holistic wealth management starts here
Join thousands of advisors who use Vanilla to transform their service offering and accelerate revenue growth.